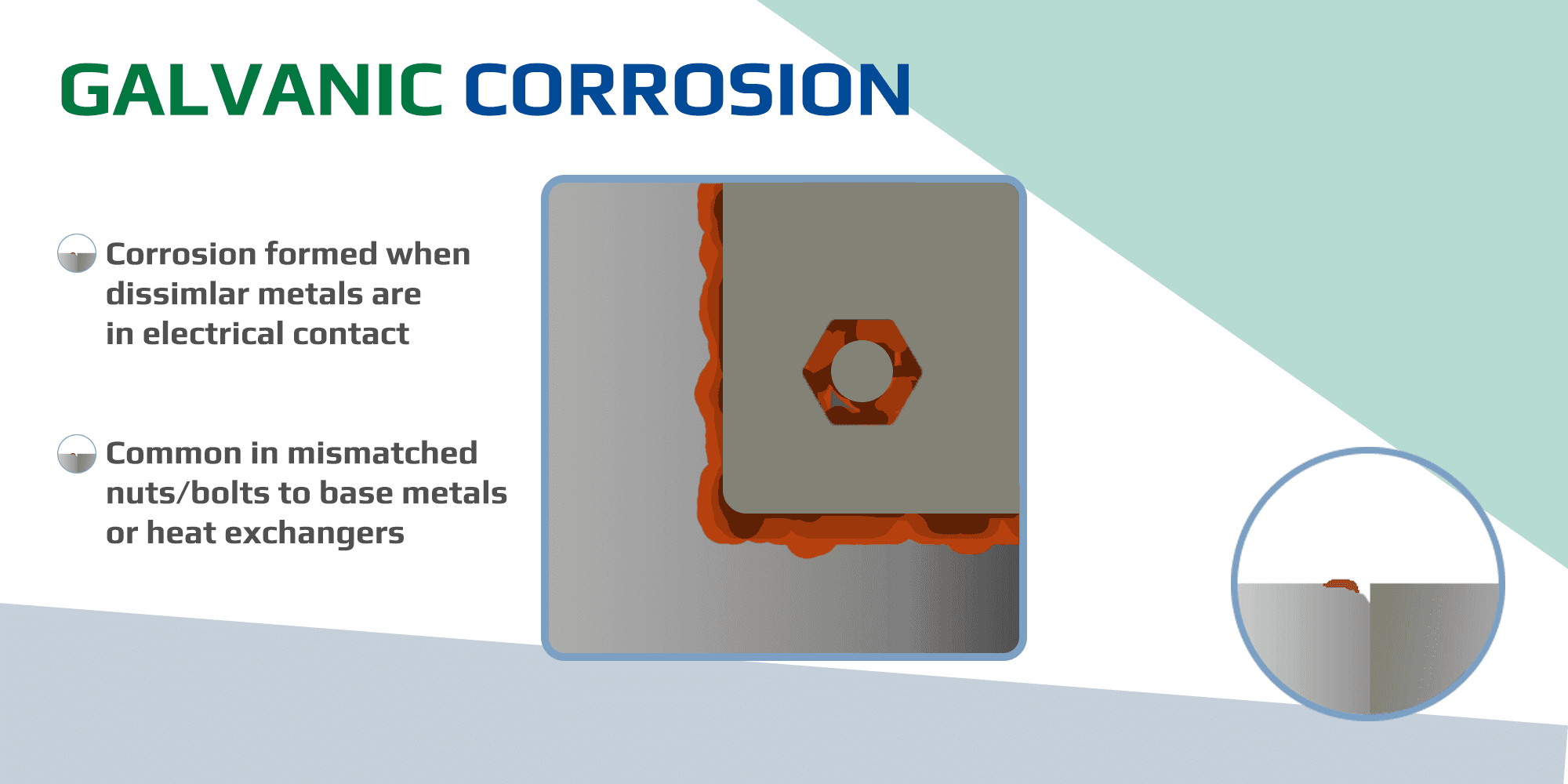
Galvanic corrosion is a form of accelerated, localized degradation that occurs when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact within an electrolyte, leading to rapid material loss on the less noble metal. Distinct from uniform corrosion, which erodes surfaces evenly (as detailed in our article on uniform corrosion), galvanic corrosion exploits electrochemical differences to create a battery-like effect, often resulting in unexpected failures in critical assemblies.
What is Galvanic Corrosion?
Galvanic corrosion, also referred to as bimetallic corrosion, develops when metals with varying electrochemical potentials are joined, forming a galvanic cell. The more active metal acts as the anode and corrodes preferentially, while the nobler metal serves as the cathode and gains protection. This process is exacerbated in conductive environments like seawater or humid atmospheres, where ions facilitate electron flow. It commonly affects alloys such as steel, aluminum, and copper in settings where material mismatches are unavoidable, such as structural joints or equipment interfaces.
Causes of Galvanic Corrosion
Key factors driving galvanic corrosion include:
- Electrochemical Potential Differences: Metals ranked far apart in the galvanic series (e.g., aluminum and copper) create strong driving forces for corrosion.
- Electrical Contact: Direct physical connection or conductive pathways allow electron transfer between the dissimilar metals.
- Presence of Electrolytes: Moisture, salts, or contaminants provide the medium for ionic conduction, intensifying the reaction.
- Surface Area Ratios: A small anode paired with a large cathode accelerates degradation on the anodic metal.
- Environmental Conditions: High humidity, temperature fluctuations, or exposure to aggressive media like chlorides promote initiation.
Effects of Galvanic Corrosion
The consequences of galvanic corrosion can be severe and far-reaching:
- Localized Material Loss: Rapid pitting or thinning at contact points weakens components, leading to leaks or structural collapse.
- Operational Downtime: Failures in heat exchangers, pipelines, or fasteners necessitate costly shutdowns and repairs.
- Safety Risks: In industries like oil & gas or marine, compromised integrity can result in hazardous incidents.
- Economic Impact: Increased maintenance expenses and reduced equipment lifespan strain budgets.
- Environmental Concerns: Corrosion byproducts may contaminate surroundings, complicating compliance with regulations.
Prevention with VCI Technology
Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor (VCI) technology provides a robust defense against galvanic corrosion by interrupting electrochemical reactions at the molecular level. GreenVCI’s proprietary VCI products, developed since 1994, release vapor-phase inhibitors that form a protective barrier on all metal surfaces, even in hard-to-reach areas like bolted joints or exchanger tubes. These solutions are particularly effective for multi-metal systems, offering sustainable protection without altering component designs. As a vertically integrated provider, GreenVCI ensures high-quality, plant-based formulations that are fully biodegradable and safe for global industries.
Key advantages include:
- Broad Compatibility: Protects diverse metals including steel, aluminum, and copper without favoring one over another.
- Eco-Conscious Design: Nitrite-free, non-toxic, and food-grade options support environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance.
- Ease of Application: Vapor delivery penetrates assemblies during storage, shipping, or operation, eliminating the need for oils or coatings.
- Cost Savings: Reduces repair frequency and extends asset life, minimizing overall ownership expenses.
Conclusion
Galvanic corrosion presents distinct challenges due to its electrochemical nature and potential for rapid, targeted damage, but awareness of its mechanisms enables effective mitigation. Integrate GreenVCI’s advanced VCI technology to safeguard your assets reliably and sustainably. Explore our full lineup of corrosion inhibitors at GreenVCI to keep your operations rust-free.